The promise of AI vision - A glimpse into the future of multimodality
I was drawing a blank.
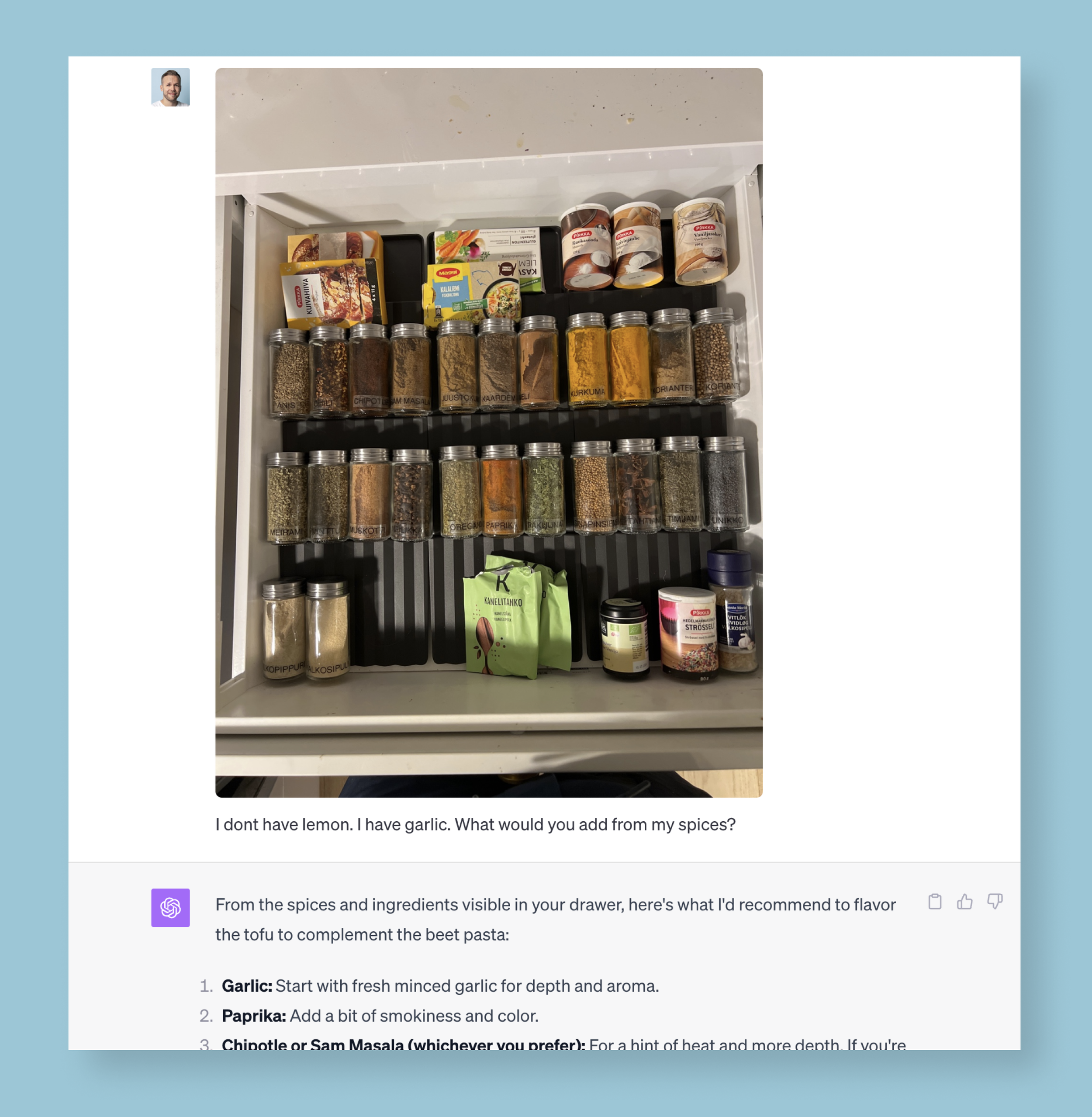
How should I season tofu to complement the beet pasta I’m cooking?
Lately, my instinct for tackling big and small questions has been to turn to AI.
I took out my phone and snapped a photo of my spice drawer. GPT-4, now equipped with vision, could recommend the exact spices from my collection to go with my pasta. It could analyze the contents of my spice rack and how they would fit into the dish I was cooking.
GPT with vision could give me highly personalized and relevant cooking instructions based on a photo of my spice rack.
Ok I admit, I mostly shared the photo to show off my newly organized spice drawer. But what do my seasoning challenges have to do with anything?
ChatGPT has been rolling out GPT-Vision to its paid users over the last few weeks. Now, you can share images with the AI and discuss them. Suddenly, AI chatbots like ChatGPT can see, hear, and read.
In this article, I’ll explore the opportunities of AI vision for designing services in three categories:
Ideation - sparring with AI using images
Instructions - getting detailed help with images
Feedback - using images with AI for on-the-spot feedback
1. Ideation - sparring with AI using images
Coming up with new ideas is a messy process. Models like GPT-4 are already useful in churning out massive amounts of ideas or elaborating on your ideas. With images, you have a whole new context for exploring ideas.
Here are some examples of using GPT-vision for ideation:
sharing a picture of post-it notes from a brainstorm and asking the AI to elaborate on them
taking a picture of kitchen appliances and asking for feature ideas for an app to complement them
giving the AI a picture of an early sketch of a user flow and asking for ideas to improve it
AI paired with vision can help you expand on post-it ideation
Based on my experimentation, GPT-4 is adept at reading even the worst handwriting. It understands all the text and other information in pictures. From there, you have all the powers of the language model at your disposal.
2. Instructions - getting detailed and relevant help
I had a small annoying issue on my website recently. The images on my Designer 2.0 training site were not aligning perfectly.
In the past, I would’ve tried googling an answer and fumbling to describe the issue.
Now, I just took a screenshot and asked GPT-4 what could be the issue. It immediately understood the problem and suggested a few steps to remedy it.
GPT-4V helped me troubleshoot a small issue on my website
What are the broader implications of this contextual visual guidance?
An elevator business could empower its employees with an AI tool that can see and access all of their internal knowledge. Many problems in the real world are easier to describe with a picture than words - including fixing complex machines like elevators.
On the consumer side, a company selling kitchen renovations could ask customers to snap photos of their space and provide highly specific product and design recommendations.
It’s also evident that these vision powers could have enormous potential in healthcare - with the obvious risks and downsides.
3. Feedback - no more working in a vacuum
The best way to improve our quality of work is to get frequent and thoughtful feedback.
Sometimes, we don’t have immediate access to a human that can give us on-the-spot helpful feedback. Also, human feedback can be great, but it can be too nice or not based on expertise.
Over the last few weeks, I’ve been experimenting with using GPT-4V for feedback. The results are promising.
You can share an early version of an app design, even a complete user journey, and ask GPT-4 for feedback. As with other prompting, providing some context and constraints to point the AI in the right direction is helpful.
GPT-4V gave detailed and useful feedback on how to improve the Workouts sections of the Nike Training app
You can ask GPT-4V to give you feedback on certain design aspects (ie. how to use gamification elements) or assign a role to the AI (you’re a financial analyst trying to use this dashboard).
Does this make all human feedback and user testing worthless?
Of course not. Feedback from an AI can help nudge us in the right direction when we don’t have access to relevant human feedback.
What’s the future of AI vision?
It’s clear now that the future of AI models is multimodality - the best models can read, hear, speak, and now see. With DALL-E 3 in ChatGPT they can also create images. The race of the multimodals will only big up speed with the launch of Google’s Gemini this fall.
What will be the future interplay of these modalities? What will it mean for how these systems can develop themselves? How can we use these capabilities to work smarter and design better products and services?
Just a few weeks into exploring AI vision, it’s easy to see how this newfound ability has interesting potential. Like with most things AI, we’ve just started to dig out the vast majority of the opportunities and risks.
Let me know if you’ve been experimenting with AI vision personally or in your company.